Day 1: Your AI agent's first phone call

How to build your first AI phone caller agent in 15 minutes. Your code. Real calls.
Let your AI make real phone calls
Your AI agent is trapped.
It can write emails. Answer questions. Generate code.
But it is stuck in your chat text box. It can't pick up a phone and call someone.
But what if it could?
What if you could say:
"Hey ChatGPT, call the restaurant and book me a table at 7pm"
or
"Hey ChatGPT, call the doctor's office and reschedule my appointment"
What if your AI agent could exist in the REAL world and not just in your browser?
That's what we're building.
✅ From scratch
✅ With your own code
✅ Deployed to AWS
A phone calling AI agent that you own and control.
Over the next 24 days, you're going to build an AI phone agent and deploy it to production.
Today? Your AI agent makes its first call. To you.
Here's a preview ⬇️
Day 14 preview: The AI agent calls me to book a dinner reservation 🤖📞
Let's build 🚀
What you'll build today
A working AI phone agent that:
✅ Calls any phone number
✅ Greets you when you answer
✅ Has a natural conversation using OpenAI's GPT
✅ Responds intelligently to what you say
All running from your laptop.
Tomorrow, we'll teach it to book restaurant reservations.
But today? Just pure magic, making it work and call you.
What you'll learn
- How OpenAI's Realtime API enables voice conversations
- Why websockets are essential (not regular HTTP)
- How Twilio connects phone calls to your code
- The role of
ngrokin development - Why this won't work for production (and what we'll build instead)
But if you want:
✅ Complete codebase (one clean repo)
✅ Complete walkthroughs
✅ Support when stuck
✅ Production templates
✅ Advanced features
Join the waitlist for the full course (launching February 2026):
Building something with AI calling? Let's chat about your use case! Schedule a free call ↗ - no pitch, just two builders talking.
Time required
15-20 minutes
Prerequisites
Before we start, you'll need:
1. Python 3.9 installed
Check your version:
python --version
Should show 3.9 or higher
2. A Twilio account
- Sign up at twilio.com/try-twilio ↗
- Get your Account SID and Auth Token from the Twilio Console ↗
- Buy a phone number with Voice capabilities ($1-2/month)
3. An OpenAI API key
- Sign up at platform.openai.com ↗
- Add $5 credit to your account
- Generate an API key from API Keys page ↗
4. ngrok (for local tunneling)
- Download from ngrok.com/download ↗
- Free tier works
5. A phone to receive the call
Using Twilio's free tier, you can only call:
- Numbers you've verified as Verified Caller IDs↗, OR
- Twilio Dev Phone↗ (virtual phone in browser)
In this tutorial we'll go with numbers we've verified.
Quick setup: Verify your personal phone, takes 2 minutes.
Step 1: Set up your project
Create a project directory and a virtual environment.
Run this in your terminal to create a new project folder:mkdir ai-caller
cd ai-caller
python -m venv venv
Activate the virtual environment
- macOS/Linux
- Windows
source venv/bin/activate
.\venv\Scripts\activate
Step 2: Install dependencies
Run this snippet to install dependencies:pip install fastapi uvicorn twilio websockets python-dotenv
What you just installed:
- FastAPI: Handles WebSocket connections
- uvicorn: Runs your web server
- twilio: Twilio Python SDK
- websockets: Connects to OpenAI's Realtime API
- python-dotenv: Manages environment variables
Step 3: Store your credentials
Run this from the root project folderai-caller:
touch .env
Open your IDE
Open the.env file in your IDE.
Add your credentials to the .env file:
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID="ACxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN="your_auth_token_here"
TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER="+1234567890"
OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-proj-xxxxxxxxxxxxx"
NGROK_DOMAIN=""
PORT=6060
Leave NGROK_DOMAIN empty for now, we'll fill in step 5.
Add .env to .gitignore to avoid adding it to Github:
echo ".env" >> .gitignore
echo "venv/" >> .gitignore
Step 4: Write the code
Create a new file called :touch simple_caller.py
simple_caller.py:
# simple_caller.py - Your First AI Caller Agent
# Day 1 of "Let Your AI Agent Make Real Phone Calls"
import os
import json
import asyncio
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket
from fastapi.websockets import WebSocketDisconnect
from twilio.rest import Client
import websockets
import uvicorn
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# Credentials
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID = os.getenv('TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID')
TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN = os.getenv('TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN')
TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER = os.getenv('TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER')
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
NGROK_DOMAIN = os.getenv('NGROK_DOMAIN')
PORT = int(os.getenv('PORT', 6060))
# AI personality
SYSTEM_MESSAGE = (
"You're a friendly AI assistant. "
"Keep responses brief and natural. "
"Ask one question at a time."
)
VOICE = 'alloy'
TEMPERATURE = 0.8
app = FastAPI()
twilio_client = Client(TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID, TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN)
@app.get('/health')
def health():
return {'status': 'ready'}
@app.websocket('/media-stream')
async def handle_media_stream(websocket: WebSocket):
"""Handle WebSocket connections between Twilio and OpenAI."""
print("Client connected")
await websocket.accept()
async with websockets.connect(
'wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17',
additional_headers={
"Authorization": f"Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}",
"OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1"
}
) as openai_ws:
await initialize_session(openai_ws)
stream_sid = None
async def receive_from_twilio():
"""Receive audio from Twilio, send to OpenAI."""
nonlocal stream_sid
try:
async for message in websocket.iter_text():
data = json.loads(message)
if data['event'] == 'start':
stream_sid = data['start']['streamSid']
print(f"📞 Call connected: {stream_sid}")
elif data['event'] == 'media':
audio_append = {
"type": "input_audio_buffer.append",
"audio": data['media']['payload']
}
await openai_ws.send(json.dumps(audio_append))
except WebSocketDisconnect:
print("Call ended")
if openai_ws.open:
await openai_ws.close()
async def send_to_twilio():
"""Receive AI audio from OpenAI, send to Twilio."""
nonlocal stream_sid
try:
async for openai_message in openai_ws:
response = json.loads(openai_message)
if response['type'] == 'response.audio.delta' and response.get('delta'):
audio_delta = {
"event": "media",
"streamSid": stream_sid,
"media": {"payload": response['delta']}
}
await websocket.send_json(audio_delta)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
await asyncio.gather(receive_from_twilio(), send_to_twilio())
async def initialize_session(openai_ws):
"""Configure OpenAI's voice settings."""
session_update = {
"type": "session.update",
"session": {
"turn_detection": {"type": "server_vad"},
"input_audio_format": "g711_ulaw",
"output_audio_format": "g711_ulaw",
"voice": VOICE,
"instructions": SYSTEM_MESSAGE,
"modalities": ["text", "audio"],
"temperature": TEMPERATURE,
}
}
print('Configuring AI voice...')
await openai_ws.send(json.dumps(session_update))
def make_call(phone_number: str):
"""Initiate the phone call via Twilio."""
if not NGROK_DOMAIN:
print("❌ ERROR: NGROK_DOMAIN not set!")
print("Run ngrok first, then update .env")
return
twiml = (
f'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>'
f'<Response><Connect><Stream url="wss://{NGROK_DOMAIN}/media-stream" /></Connect></Response>'
)
call = twilio_client.calls.create(
to=phone_number,
from_=TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER,
twiml=twiml
)
print(f'📞 Calling {phone_number}...')
print(f'📞 Call SID: {call.sid}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("❌ Usage: python simple_caller.py +1234567890")
sys.exit(1)
phone_number = sys.argv[1]
make_call(phone_number)
print("🚀 Starting server on port 6060...")
print("💡 Make sure ngrok is running!")
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=PORT)
Learn what we did.
1. Setup & configuration
load_dotenv()loads secrets from.env.- We pull in:
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID,TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN,TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBEROPENAI_API_KEYNGROK_DOMAINPORT(defaults to6060)
SYSTEM_MESSAGE,VOICE,TEMPERATUREdefine the AI's phone persona.app = FastAPI()creates the web app.twilio_client = Client(...)is the Twilio SDK used to start calls.
/health is a simple readiness check Twilio (or you) can hit to see if the server is alive.
2. WebSocket bridge: Twilio ↔ OpenAI
@app.websocket('/media-stream')
async def handle_media_stream(websocket: WebSocket):
This endpoint is where Twilio connects via WebSocket when the call is live.
Inside it we:
-
Accept the WebSocket from Twilio:
await websocket.accept() -
Open a second WebSocket to OpenAI Realtime with
websockets.connect(...) -
Call a
wait initialize_session(openai_ws)to configure the AI voice session
Then we define two async tasks:
1. receive_from_twilio()
-
Listens to incoming messages from Twilio:
-
On
event == "start": we capturestream_sid(call stream ID) -
On
event == "media": we extract the audio payload and send this:
-
{"type": "input_audio_buffer.append", "audio": ...}
To OpenAI over openai_ws
- On disconnect (
WebSocketDisconnect): we log "Call ended" and close OpenAI if still open.
2. send_to_twilio()
-
Listens to messages coming back from OpenAI (
async for openai_message in openai_ws) -
When we see
response.audio.deltawith adeltafield:- We wrap that audio in Twilio's format:
{"event": "media", "streamSid": stream_sid, "media": {"payload": response['delta']}}
- And send it back over
websocket.send_json(...)to Twilio.
Running both directions in parallel
await asyncio.gather(receive_from_twilio(), send_to_twilio())
This is what creates a full-duplex audio stream:
Phone → Twilio → Laptop → OpenAI
OpenAI → Laptop → Twilio → Phone
3. AI session configuration
async def initialize_session(openai_ws):
This tells OpenAI how to behave:
-
turn_detection: server_vad→ OpenAI detects when the caller stops speaking -
input_audio_format/output_audio_format="g711_ulaw"→ matches Twilio's phone audio -
voice,instructions,temperature,modalities→ style + behavior
4. Starting the call with Twilio
def make_call(phone_number: str):
This function:
-
Checks that
NGROK_DOMAINis set; if not, it bails out -
Builds a TwiML response:
<Response>
<Connect>
<Stream url="wss://NGROK_DOMAIN/media-stream" />
</Connect>
</Response>
This tells Twilio: "When the call is answered, open a WebSocket to this URL."
- Calls:
twilio_client.calls.create(to=phone_number, from_=TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER, twiml=twiml)
which dials the user and wires the call into our /media-stream endpoint.
We log the target number and Call SID for debugging.
5. Script entrypoint
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
Reads the phone number from
sys.argv[1] -
Calls
make_call(phone_number)to initiate the Twilio call -
Starts FastAPI with Uvicorn:
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=PORT)
So one command:
python simple_caller.py +1234567890
does three things:
-
Starts your local WebSocket server
-
Opens a public tunnel via ngrok (you already configured the domain)
-
Tells Twilio to dial your number and stream audio into your AI agent
Step 5: Start ngrok
Open a new terminal window and run:ngrok http 6060
You'll see prints similar to this in your terminal:
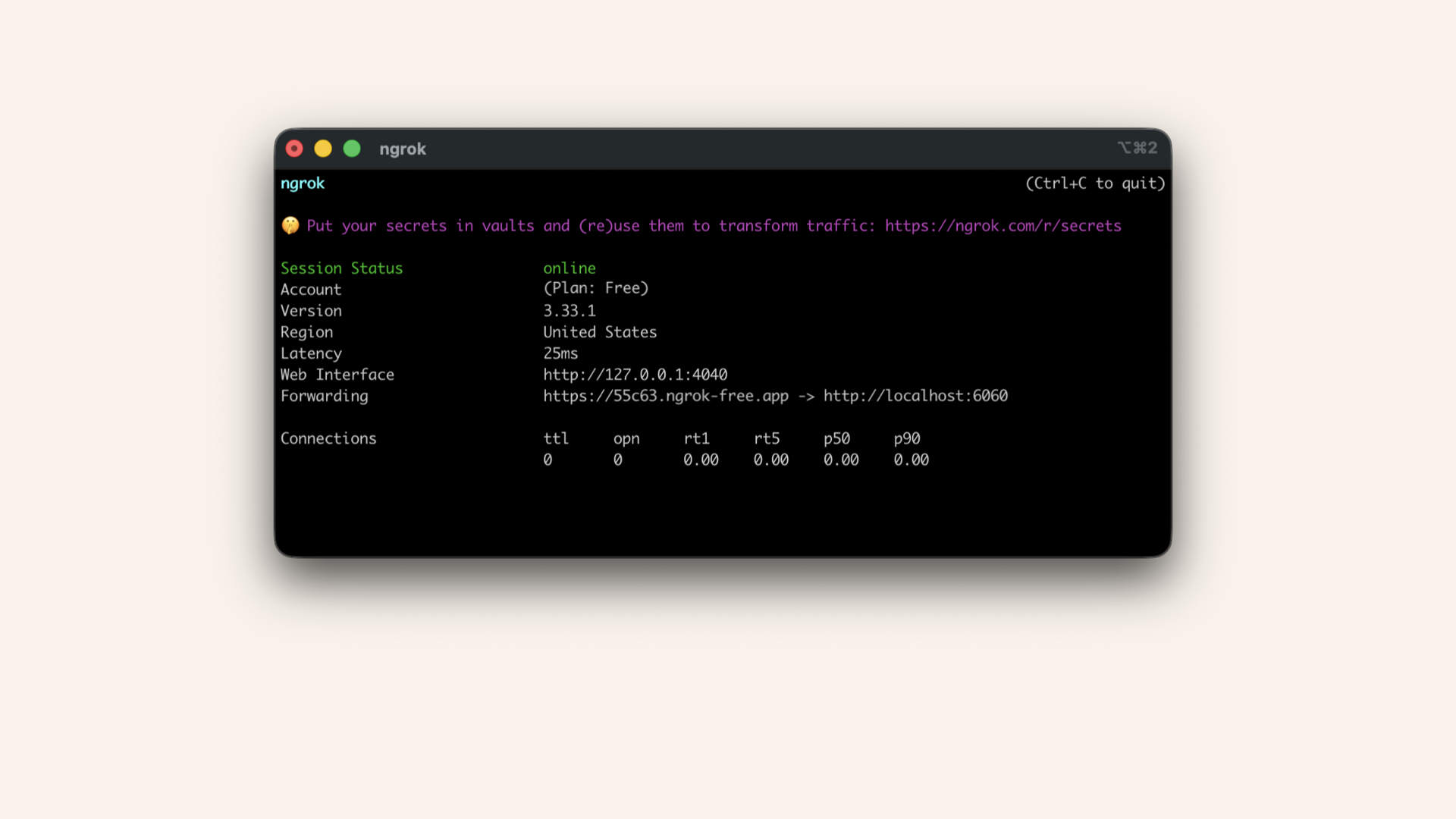
You'll see ngrok running in your terminal
Copy the domain without https://:
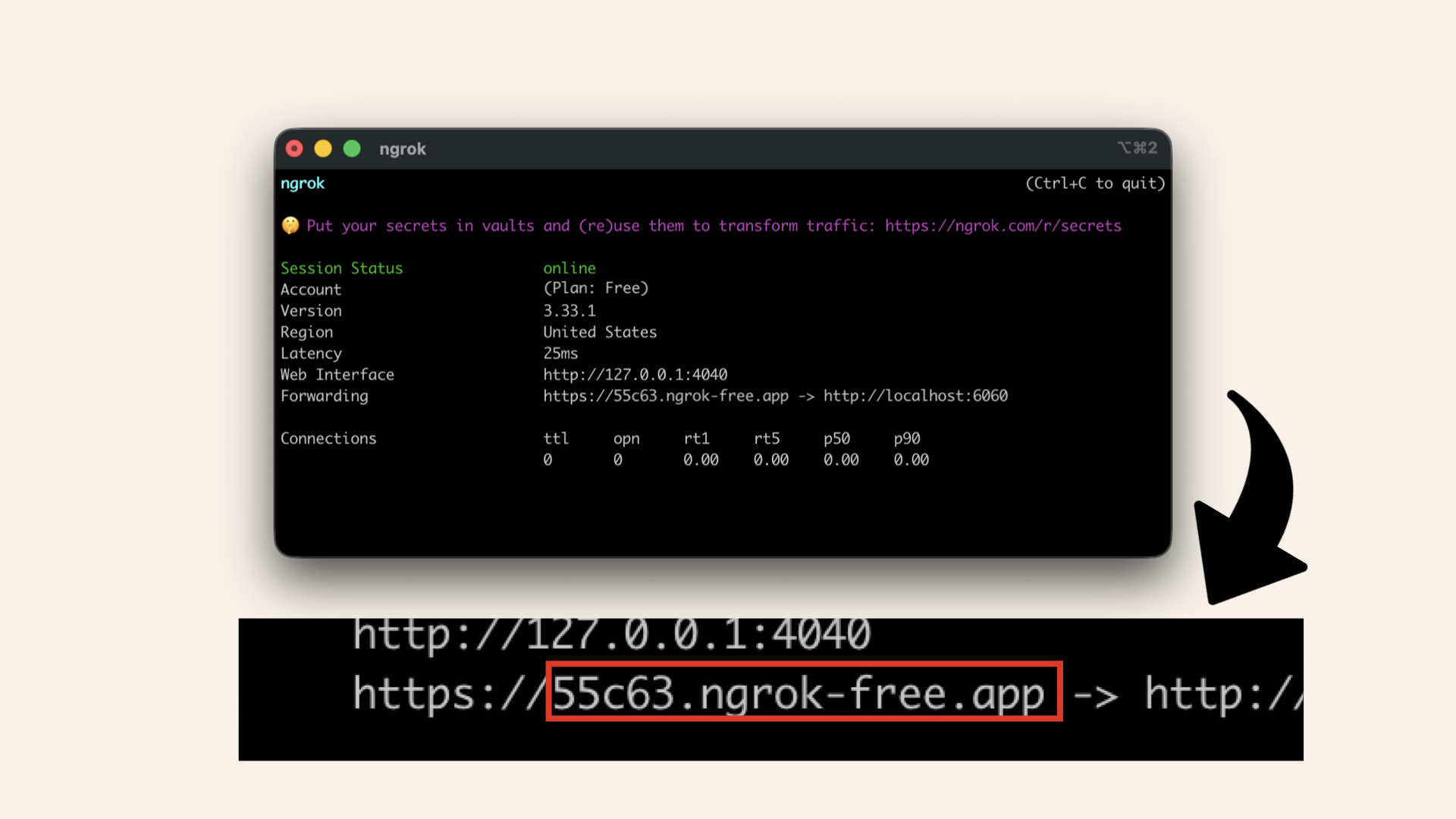
Copy the domain without https://
Step 6: Update .env with ngrok url
.env again and add the ngrok domain:
NGROK_DOMAIN="YOUR_NGROK_DOMAIN"
Step 7: Make your first call 📞
Run this in your main terminal window (with your virtual environment activated) but with your own phone number:python simple_caller.py +1234567890
Make sure to change +1234567890 to your own phone number
✅ Success check
You should see:
📞 Calling +1234567890...
📞 Call SID: CAxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
🚀 Starting server on port 6060...
INFO: Started server process [10328]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:6060
And your phone rings 🎉
Answer it. Say hello. The AI agent responds!
If everything worked:
✅ Your phone rang
✅ AI greeted you
✅ AI responded to what you said
✅ Conversation felt natural
✅ Terminal shows "Call connected"
You just gave your AI agent a voice in the real world
Troubleshooting
Phone doesn't ring
Check 1: Is ngrok running?
In ngrok terminal window, you should see:
# Forwarding https://xxxxx.ngrok.app -> http://localhost:6060
Check 2: Did you update NGROK_DOMAIN in .env?
Check 3: Is the number in E.164 format?
# ✅ Correct: +14155551234
# ❌ Wrong: 4155551234
Check 4: Is the number verified in Twilio?
Phone rings but no AI voice
Check 1: Look for this in main terminal window:
📞 Call connected: CAxxxxxxxxx
Check 2: Test your OpenAI API key:
Run:curl https://api.openai.com/v1/models \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY"
Check 3: Visit ngrok's web UI at http://127.0.0.1:4040
- Look for WebSocket upgrade request
- Status should be 101 (Switching Protocols)
"Module not found" error
source venv/bin/activate # macOS/Linux
.\venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
pip install fastapi uvicorn twilio websockets python-dotenv
Phone rings but hangs up when you pick up
Check 1: Did you update NGROK_DOMAIN in .env after opening a new ngrok tunnel?

Copy the domain without https://
Check 2: Log in to your Twilio account, click on the Monitor tab, then Error logs:
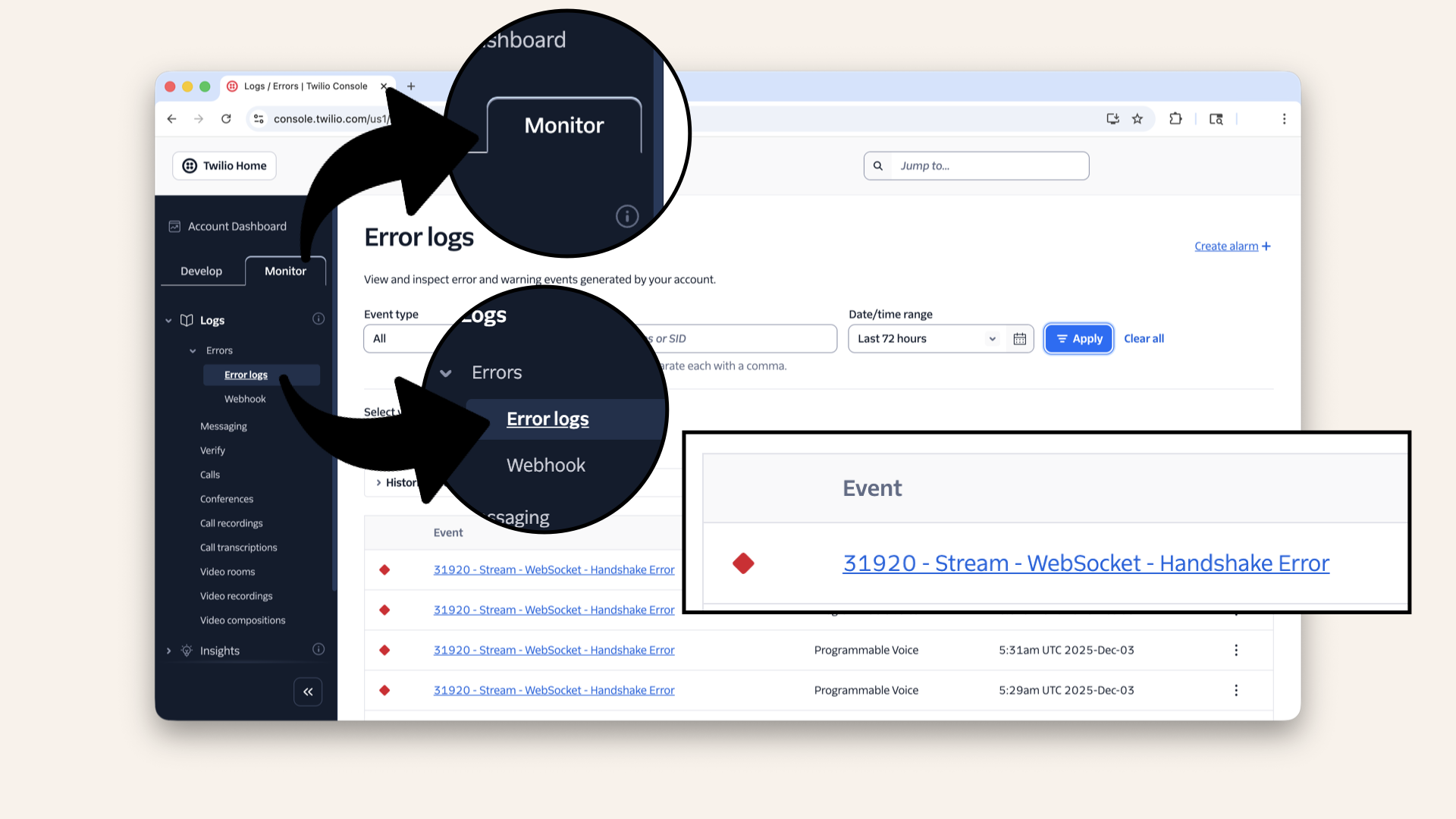
Log in to your Twilio account, click on the Monitor tab, then Error logs to check the error logs
Check 3: If the phone rings but immediately hangs up when you answer, the error Stream - WebSocket - Handshake Error likely indicates that the ngrok domain is incorrect.
Check your .env file
What did we just build?
The flow:
Key concepts
WebSockets: Stay open for continuous two-way audio streaming (unlike regular HTTP request/response)
ngrok: Creates a public tunnel to your localhost so Twilio can reach you
g711_ulaw: Phone call audio format (8kHz, compressed)
Server VAD: OpenAI detects when you stop speaking
Tomorrow's preview
Today: Your AI had a basic conversation.
Tomorrow (Day 2): We're giving it a REAL job → booking restaurant reservations.
You'll test it by answering the phone and roleplaying as a restaurant.
Your AI agent will:
- Request a reservation
- Handle follow-up questions
- Confirm details
- Sound professional
This is where it gets fun.
You'll test it by answering the phone and playing the restaurant staff.
It's hilarious and impressive at the same time.
Is this production ready? 🤔
No, this setup has some problems:
❌ When you close your laptop, it stops working
❌ When WiFi drops, calls fail
❌ ngrok URLs change on restart
❌ Can't handle multiple simultaneous calls
❌ Not production-ready
That's why we're deploying the caller agent to AWS in this advent calendar, on days 3-24.
Share your win 🎉
Got it working? Share it!
Twitter/X:
"Just built my first AI phone caller agent! It actually called me and we had a conversation. Day 1 of @norahsakal's advent calendar 🎄"
LinkedIn:
"Today I gave my AI agent a voice. It called me. We talked. This is wild. Following Norah Klintberg Sakal's 24-day advent calendar 🎄 on building production AI calling agents from scratch."
Tag me! I want to see your wins! 🎉
Want the full course?
But if you want:
✅ Complete codebase (one clean repo)
✅ Complete walkthroughs
✅ Support when stuck
✅ Production templates
✅ Advanced features
Join the waitlist for the full course (launching February 2026):
Need help with deployment? Want to brainstorm your AI calling idea? Grab a free 30-min call ↗ - happy to help.
Tomorrow
Tomorrow: Day 2 - Teach your AI agent to book restaurants 🍽️
You'll customize your AI's personality, change its voice and give it a real job: calling and booking dinner reservations.
Read Day 2 ↗
See you then!
— Norah
Learning resources that helped me
This tutorial is inspired by Twilio's excellent guide on building voice agents with OpenAI's Realtime API ↗
I took their foundational concepts and expanded them to show you:
- How to deploy to production (not just localhost)
- How to build real-world use cases (restaurant booking, etc.)
- How to own your infrastructure (AWS from scratch)
If you want to dive deeper into Twilio's API, check out their docs at twilio.com/docs ↗
But this advent calendar? It's about taking that foundation and making it REAL.
